Anaerobic batch fermentation assay for the evaluation of biogas and biomethane yield
The biomethane potential or biochemical methane potential (BMP) of a specific substrate defines the maximum amount of methane that can be produced by anaerobic digestion. The definition refers to the existing state of the sample as it is analyzed or applied in fermentation processes. The BMP is a key parameter for substrate characterization and efficiency evaluation of anaerobic digestion plants. It is crucial for assessing quality and monetary value of different substrate types and enables reliable process balancing.
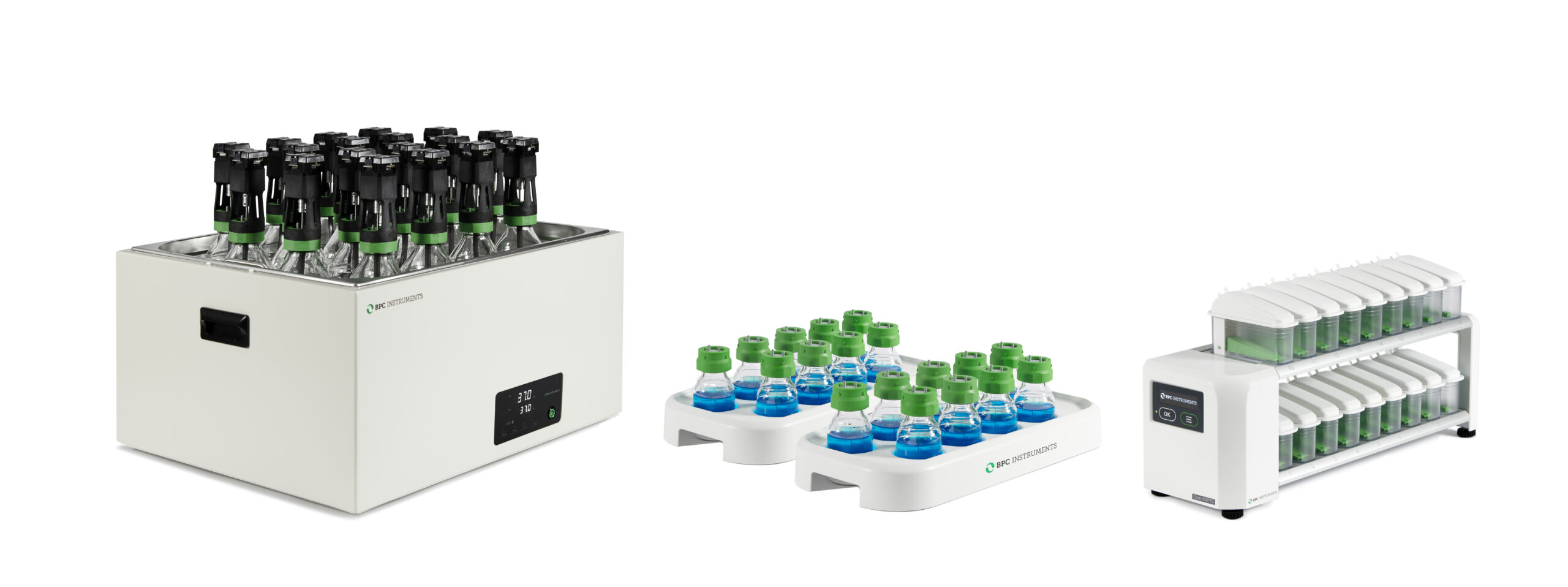
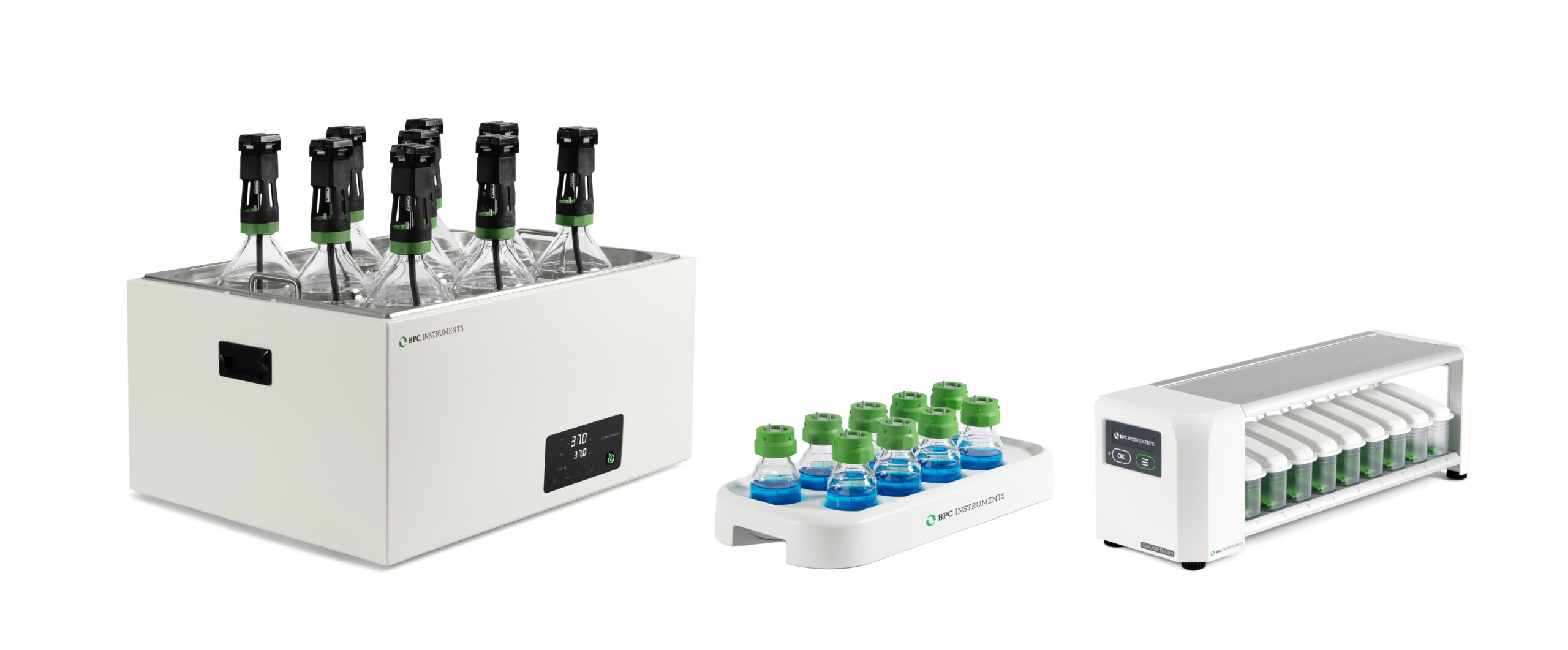
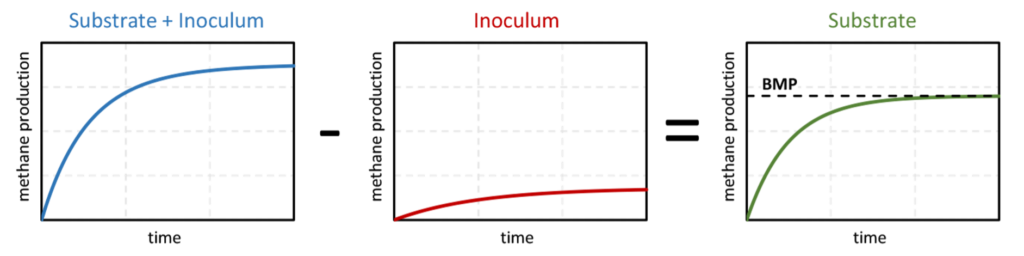
BMP is typically measured in anaerobic batch tests in a laboratory setup (BMP test). The fundamental principle of a BMP test is straight forward: A sample of the investigated substrate is digested with an active and well-functioning inoculum in bottles incubated at an appropriate temperature. Additionally, blank samples, only containing inoculum, are incubated as well. Assuming no synergistic/antagonistic effects, the resulting methane production of the substrate can be determined by subtracting methane production of the blank (inoculum) from the substrate sample (substrate + inoculum). The final value of cumulative methane production after test termination is defined as the experimental BMP of the substrate.
AMPTS® III and AMPTS® III Light are well-recognised and the recommended laboratory platforms according to the German norm VDI 4630 and several international laboratory protocols for conducting biochemical methane potential or biomethane potential (BMP), specific methanogenic activity (SMA), residual gas potential (RGP) and biohydrogen potential analyses.